STUDY DESIGN
TRIAL 1: A double-blind, placebo-controlled, Phase 3 trial in patients heterozygous for the F508del mutation and a specific mutation1,2
- Phase 3, 24-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled study assessing the efficacy of TRIKAFTA1,a
- Patients were randomized 1:1
- 200 patients received TRIKAFTA: elexacaftor 200 mg/tezacaftor 100 mg/ivacaftor 150 mg qam and ivacaftor 150 mg qpm with fat-containing food
- 203 patients received placebo q12h with fat-containing food
- All patients remained on their standard-of-care CF therapies.
Please see additional safety information based on this trial in the safety profile.
aAll patients who completed the study were eligible to roll over into a 192-week, open-label Extension Study.1,3
Key Inclusion Criteria1,2,b
- Confirmed CF diagnosis, clinically stable, and at least 12 years of age
- Heterozygous for the F508del mutation and one of approximately 200 other mutations in the CFTR gene that resulted in either:
- No CFTR protein
- A CFTR protein that lacks baseline function and is not responsive to ivacaftor and tezacaftor/ivacaftor
- ppFEV1 between 40% and 90% at screening
bKey exclusion criteria included clinically significant cirrhosis with or without portal hypertension, lung infection with organisms associated with a more rapid decline in pulmonary status (including, but not limited to, Burkholderia cenocepacia, Burkholderia dolosa, and Mycobacterium abscessus), and solid organ or hematologic transplantation.1,2
Primary Endpoint1
- Absolute change in ppFEV1 from baseline at Week 4
- Preplanned interim analysis was conducted after ≥140 patients completed the Week 4 visit and ≥100 patients completed the Week 12 visit
- There were 403 patients included in the preplanned interim analysis at Week 4
Select Secondary Endpoints1,c
- Absolute change from baseline through week 24 in ppFEV1
- Number of pulmonary exacerbations through week 24d
- Absolute change from baseline through week 24 in sweat chloride
- Absolute change from baseline through week 24 and at week 4 in CFQ-R Respiratory Domain score
- Absolute change from baseline at week 24 in BMI
cA hierarchical testing procedure was performed for key secondary endpoints. For an endpoint to be significant, both it and all previous tests in the hierarchy had to achieve P<0.05.2
dIn the trial, a pulmonary exacerbation was defined as a change in antibiotic therapy (IV, inhaled, or oral) as a result of 4 or more of 12 prespecified sinopulmonary signs/symptoms.1
Baseline Characteristics4
| TRIKAFTA (N=200) | Placebo (N=203) | |
|---|---|---|
| Sex, female, % | 48.0 | 48.3 |
| Mean age, years (range) | 25.6 (12.1-59.9) | 26.8 (12.3-64.0) |
| Mean BMI, kg/m2 (range) | 21.49 (15.01-30.86) | 21.31 (14.42-33.80) |
| Mean ppFEV1 (range) | 61.6 (33.8-97.1) | 61.3 (32.3-93.7) |
| Mean SwCI, mmol/L (range) | 102.3 (22.5-156.0) | 102.9 (68.5-137.0) |
| TRIKAFTA (N=200) | Placebo (N=203) | |
|---|---|---|
| Sex, female, % | 48.0 | 48.3 |
| Mean age, years (range) | 25.6 (12.1-59.9) | 26.8 (12.3-64.0) |
| Mean BMI, kg/m2 (range) | 21.49 (15.01-30.86) | 21.31 (14.42-33.80) |
| Mean ppFEV1 (range) | 61.6 (33.8-97.1) | 61.3 (32.3-93.7) |
| Mean SwCI, mmol/L (range) | 102.3 (22.5-156.0) | 102.9 (68.5-137.0) |
SUMMARY OF RESULTS
Trial outcomes for patients aged 12 years and older (heterozygous F508del/other specific)
Primary Endpoint2
Select Secondary Endpoints
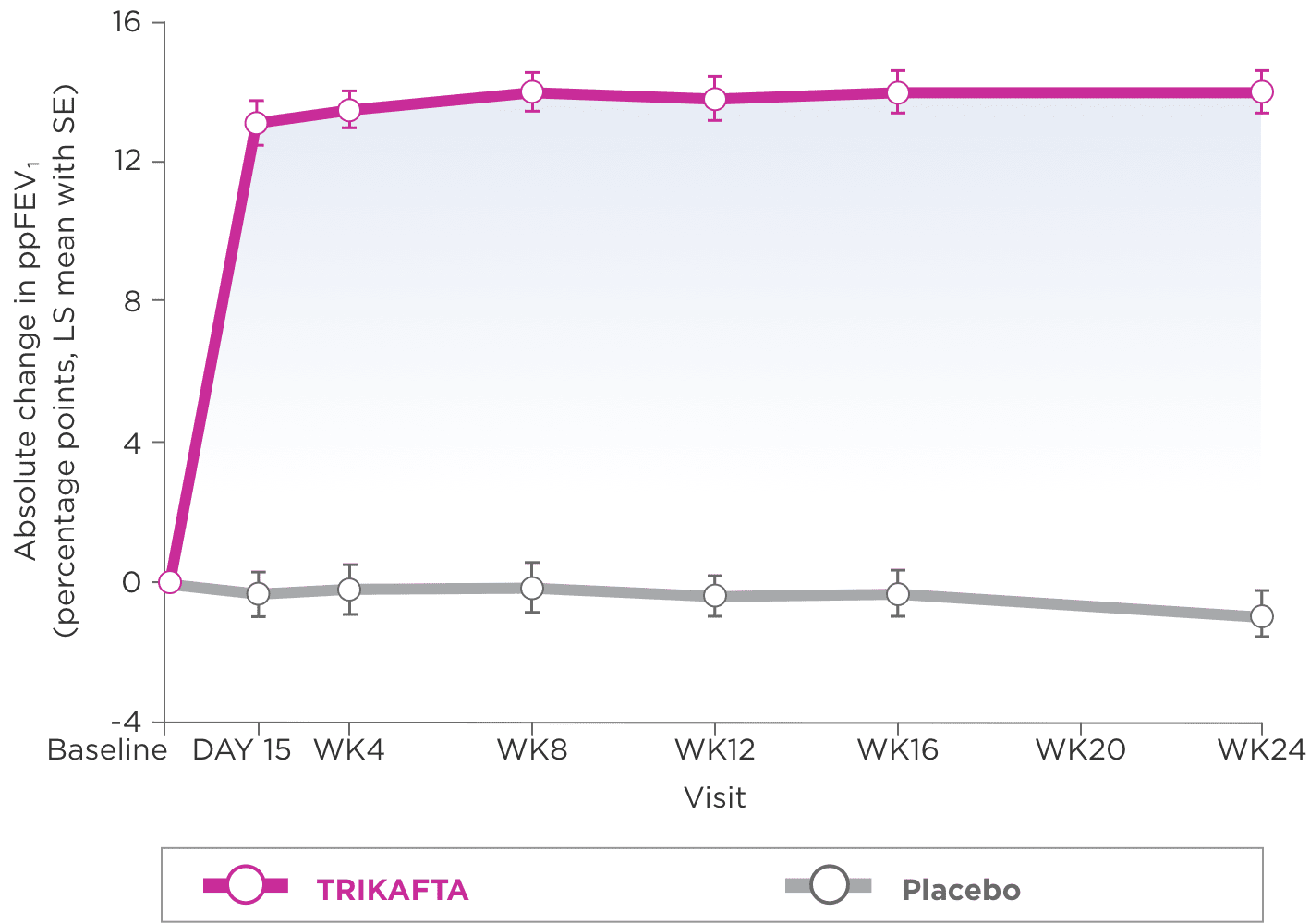
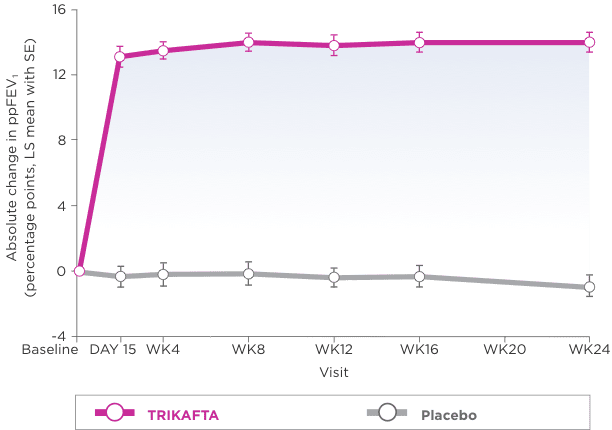
- Improvements in ppFEV1 were seen regardless of age, ppFEV1 at baseline, geographic region, and sex1
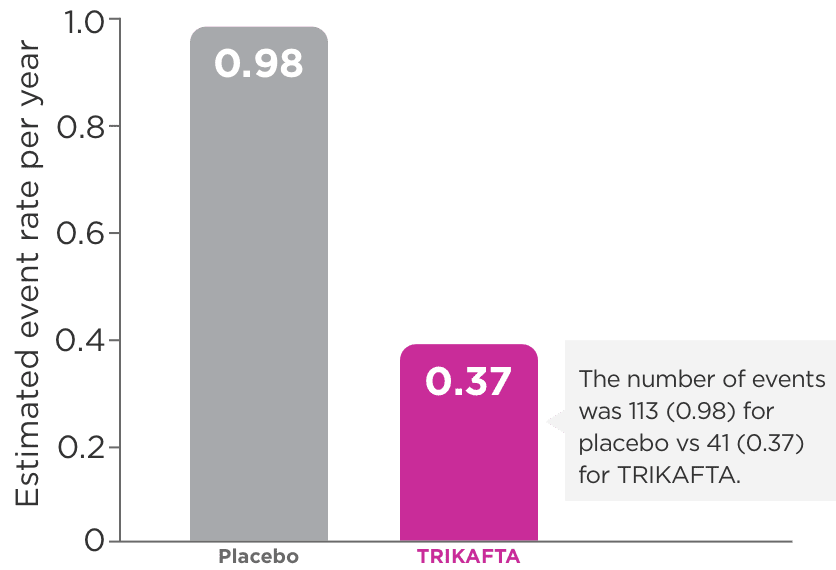
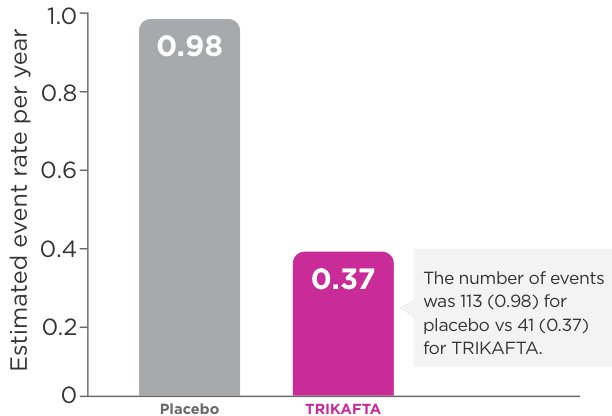
eIn Trial 1, the number of pulmonary exacerbation events was 113 (0.98) for placebo vs 41 (0.37) for TRIKAFTA.1
fIn Trial 1, the number of pulmonary exacerbations is expressed as a rate over 48 weeks based on 24 weeks of observation.1
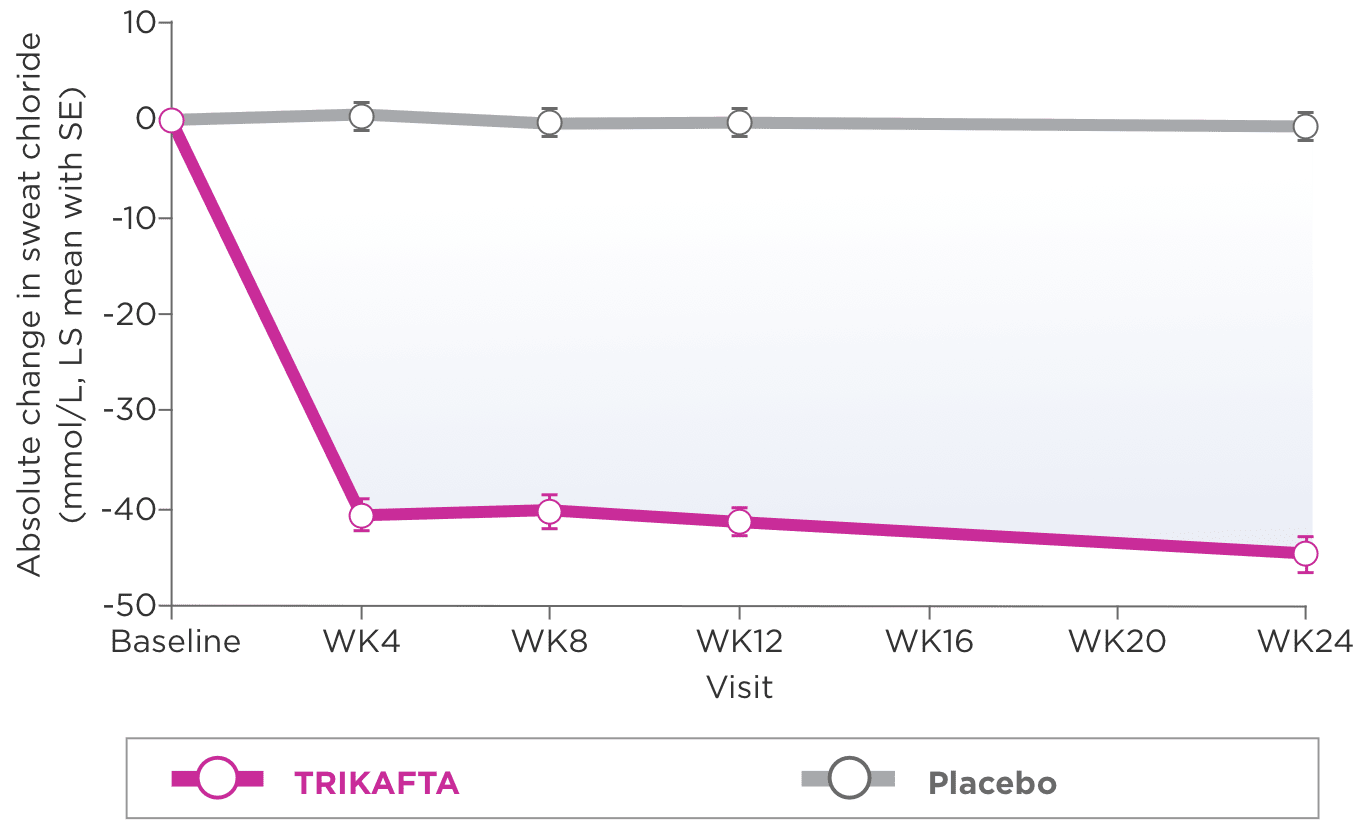
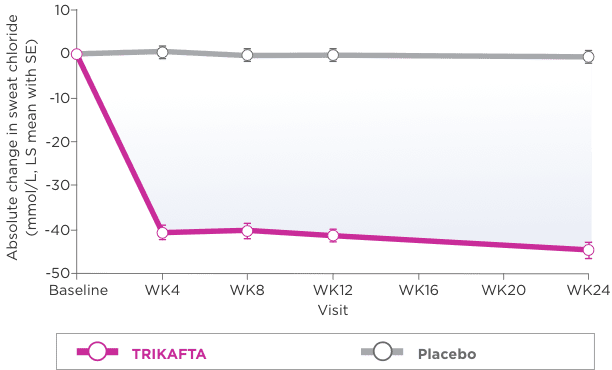
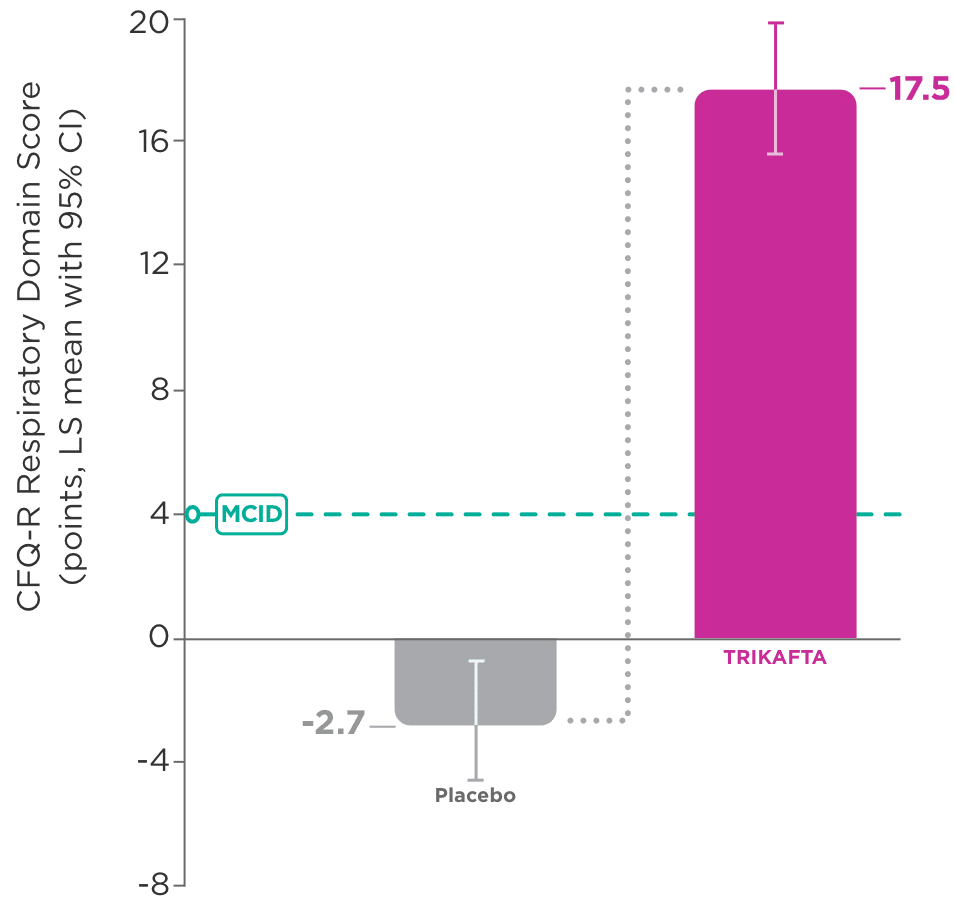
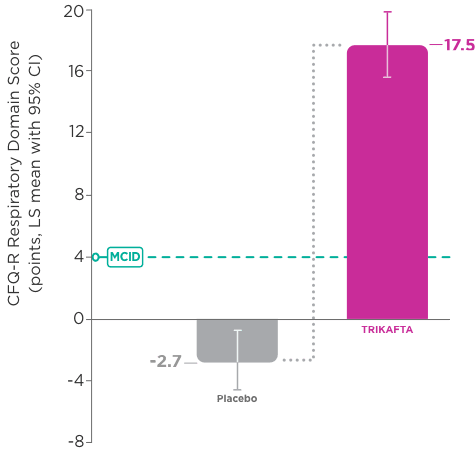
- In Trial 1, significant improvement in CFQ-R Respiratory Domain score was seen as early as Week 4
- 20.1-point improvement vs placebo (95% CI: 16.9, 23.2; P<0.0001)
- Waking up from coughing
- Wheezing
- Coughing
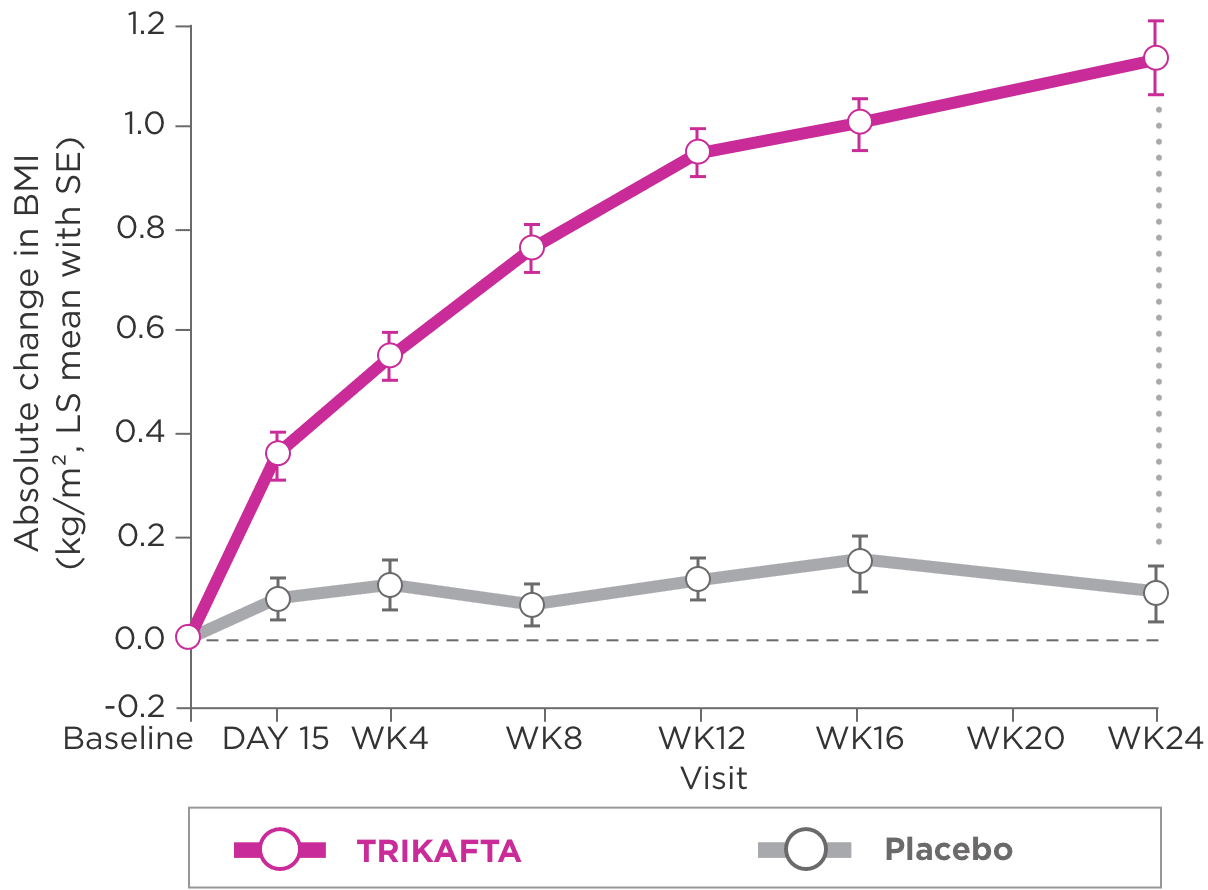
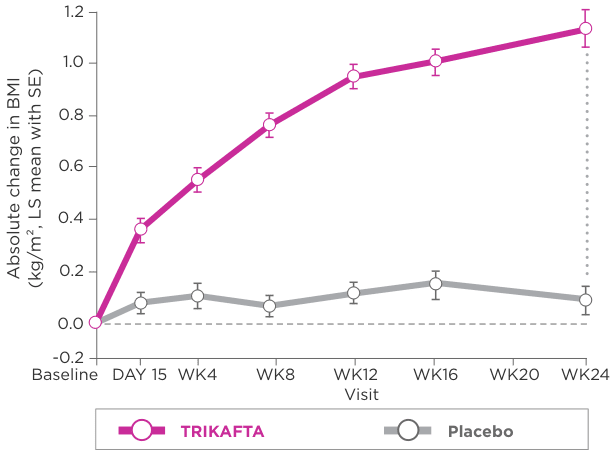
BMI, body mass index; CF, cystic fibrosis; CFQ-R, Cystic Fibrosis Questionnaire-Revised; CFTR, cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator; CI, confidence interval; IV, intravenous; lb, pounds; LS, least squares; MCID, minimal clinically important difference; ppFEV1, percent predicted forced expiratory volume in 1 second; q12h, every 12 hours; qam, every morning; qpm, every evening; RR, rate ratio, SE, standard error; SwCl, sweat chloride; WK, week.
STUDY DESIGN
TRIAL 2: A double-blind, active-controlled, head-to-head Phase 3 trial in patients homozygous for the F508del mutation1,2
- Phase 3, 4-week, double-blind, active-controlled, head-to-head study assessing the efficacy of TRIKAFTA1,a
- Prior to the run-in period, all patients in this study discontinued previous CFTR modulator therapies, but remained on their standard-of-care CF therapies.1
- During the 4-week, open-label run-in period, all patients received tezacaftor 100 mg daily/ivacaftor 150 mg q12h
- During the 4-week, double-blind treatment period, patients were randomized 1:1
- 55 patients received TRIKAFTA: elexacaftor 200 mg/tezacaftor 100 mg/ivacaftor 150 mg qam and ivacaftor 150 mg qpm with fat-containing food
- 52 patients received an active comparator: tezacaftor 100 mg/ivacaftor 150 mg qam and ivacaftor 150 mg qpm with fat-containing food
aAll patients who completed the study were eligible to roll over into a 192-week, open-label Extension Study.1,3
Key Inclusion Criteria1,2,b
- Confirmed CF diagnosis, clinically stable, and at least 12 years of age
- Homozygous for the F508del mutation
- ppFEV1 between 40% and 90% at screening
bKey exclusion criteria included clinically significant cirrhosis with or without portal hypertension, lung infection with organisms associated with a more rapid decline in pulmonary status (including, but not limited to, Burkholderia cenocepacia, Burkholderia dolosa, and Mycobacterium abscessus), and solid organ or hematologic transplantation.1,4
Primary Endpoint1
- Absolute change in ppFEV1 from baseline at Week 4
Select Secondary Endpoints1,c
- Absolute change from baseline at Week 4 in sweat chloride
- Absolute change from baseline at Week 4 in CFQ-R Respiratory Domain score
cA hierarchical testing procedure was performed for key secondary endpoints. For an endpoint to be significant, both it and all previous tests in the hierarchy had to achieve a hierarchy of P<0.05.5
Baseline Characteristics4
| TRIKAFTA (N=55) | Tezacaftor/ivacaftor and ivacaftor (N=52) | |
|---|---|---|
| Sex, female, % | 56.4 | 53.8 |
| Mean age, years (range) | 28.8 (12.7-54.1) | 27.9 (12.4-60.5) |
| Mean BMI, kg/m2 (range) | 21.8 (16.0-28.4) | 21.9 (15.6-34.6) |
| Mean ppFEV1 (range) | 61.6 (35.0-87.4) | 60.2 (35.0-89.0) |
| Mean SwCI, mmol/L (range) | 91.4 (67.0-114.0) | 90.0 (60.5-112.0) |
| TRIKAFTA (N=55) | Tezacaftor/ ivacaftor and ivacaftor (N=52) | |
|---|---|---|
| Sex, female, % | 56.4 | 53.8 |
| Mean age, years (range) | 28.8 (12.7-54.1) | 27.9 (12.4-60.5) |
| Mean BMI, kg/m2 (range) | 21.8 (16.0-28.4) | 21.9 (15.6-34.6) |
| Mean ppFEV1 (range) | 61.6 (35.0-87.4) | 60.2 (35.0-89.0) |
| Mean SwCI, mmol/L (range) | 91.4 (67.0-114.0) | 90.0 (60.5-112.0) |
SUMMARY OF RESULTS
Trial outcomes for patients aged 12 years and older (homozygous F508del mutation)
Primary Endpoint2
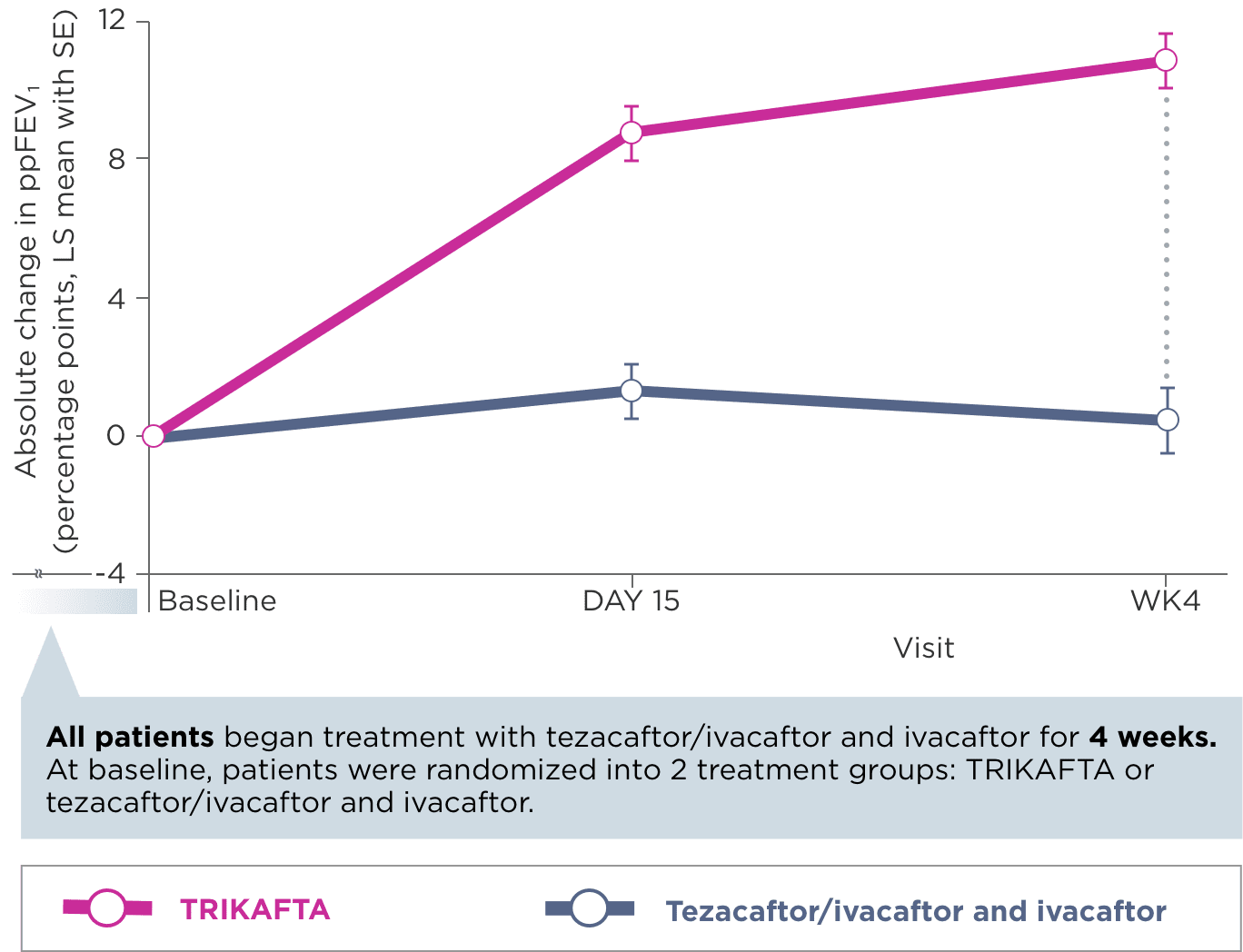
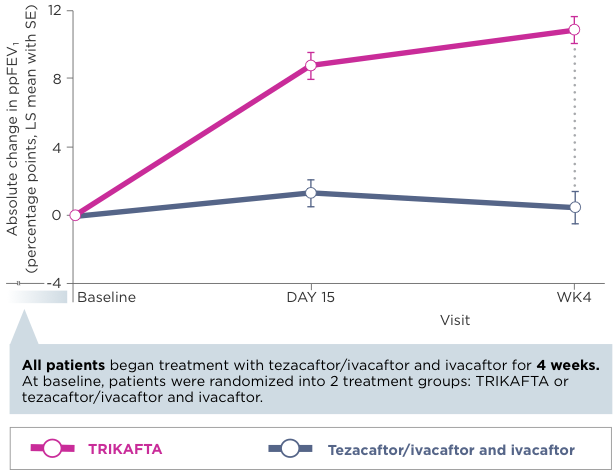
Select Secondary Endpoints
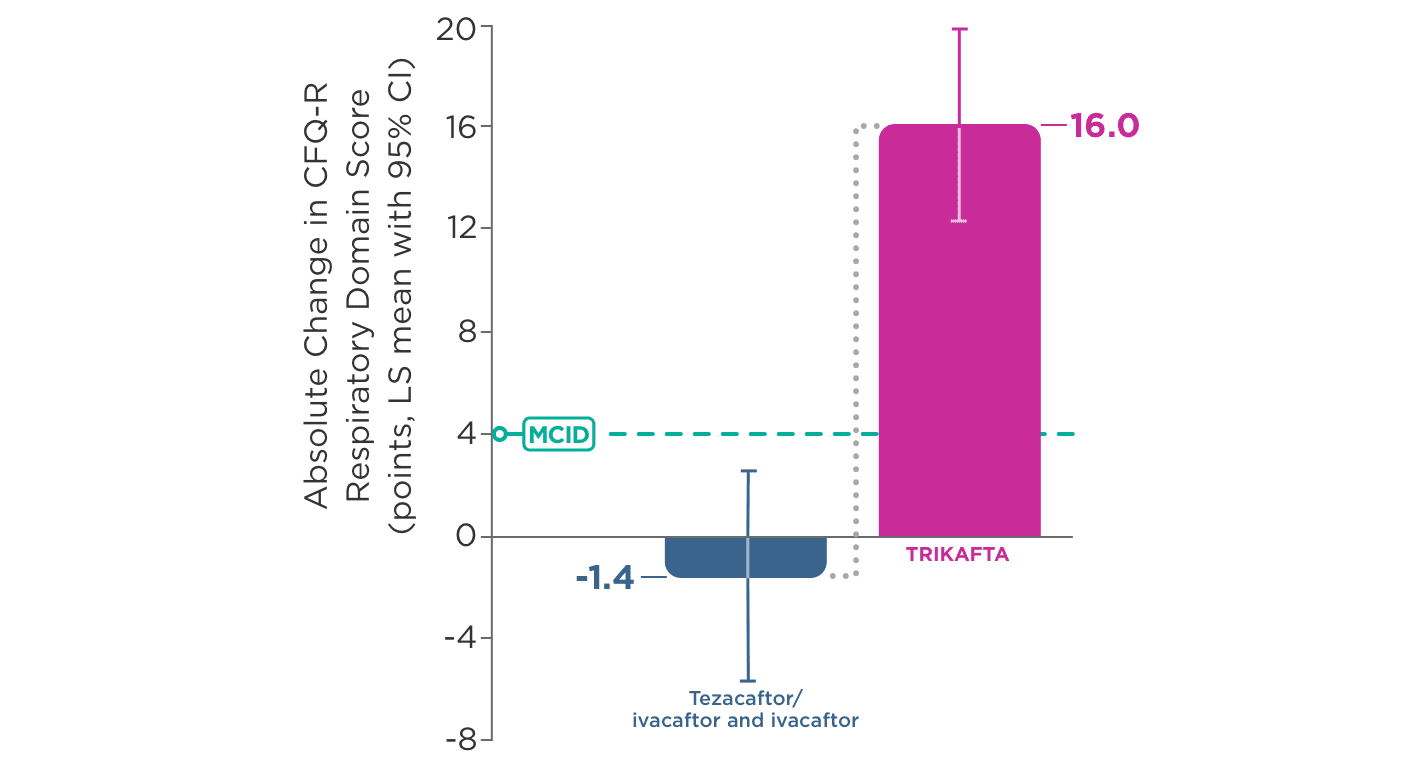
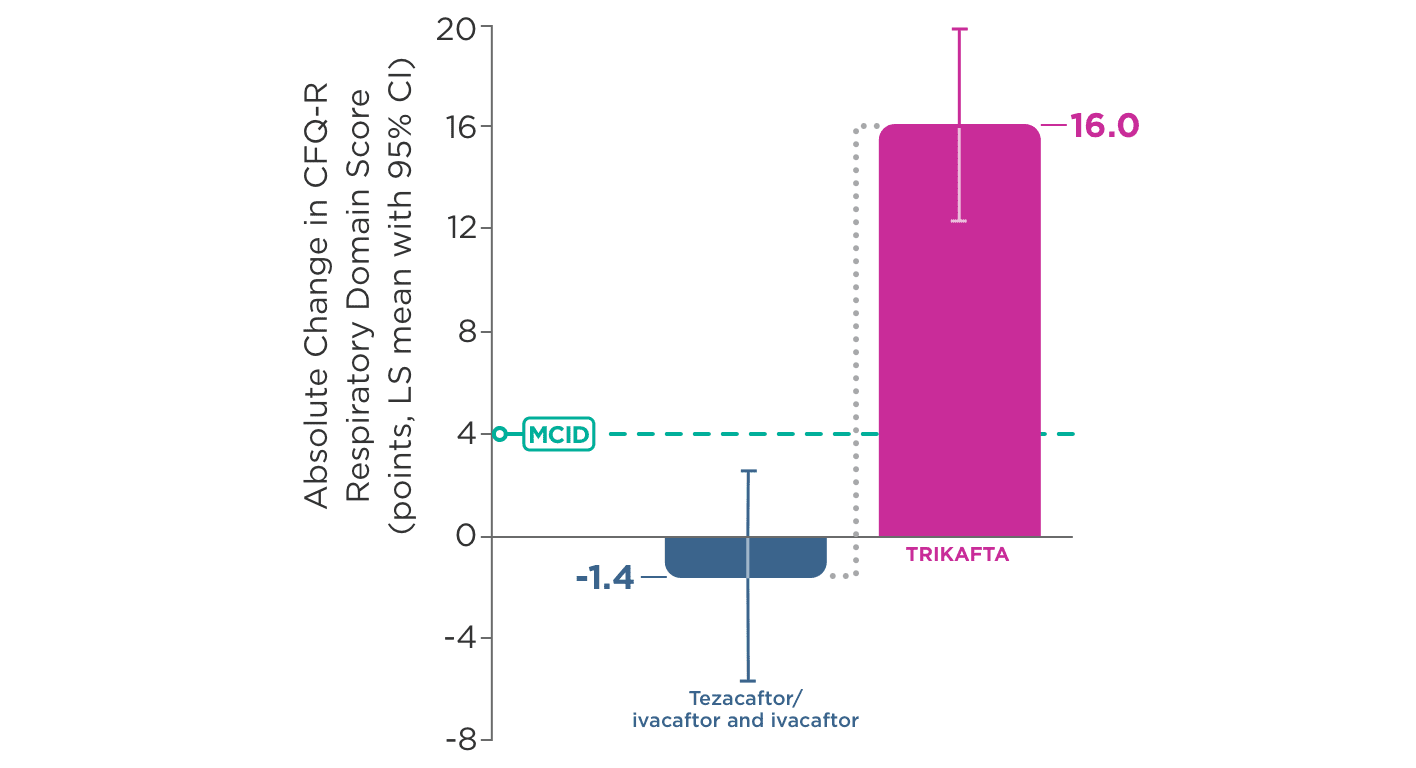
- Waking up from coughing
- Wheezing
- Coughing
BMI, body mass index; CF, cystic fibrosis; CFTR, cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator; CFQ-R, Cystic Fibrosis Questionnaire-Revised; CI, confidence interval; IV, intravenous; LS, least square; MCID, minimal clinically important difference; ppFEV1, percent predicted forced expiratory volume in 1 second; q12h, every 12 hours; qam, every morning; qpm, every evening; RR, rate ratio, SE, standard error; SwCl, sweat chloride; WK, week.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Elevated Transaminases and Hepatic Injury
- Liver failure leading to transplantation has been reported in a patient with cirrhosis and portal hypertension while receiving TRIKAFTA. Avoid use of TRIKAFTA in patients with pre-existing advanced liver disease (e.g., as evidenced by cirrhosis, portal hypertension, ascites, hepatic encephalopathy) unless the benefits are expected to outweigh the risks. If used in these patients, they should be closely monitored after the initiation of treatment
- Isolated elevations of transaminases or bilirubin have been observed in patients with CF treated with TRIKAFTA. In some instances, transaminase elevations have been associated with concomitant elevations in total bilirubin and/or international normalized ratio (INR) and have resulted in patients being hospitalized for intervention, including in patients without a history of pre-existing liver disease
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
TRIKAFTA is indicated for the treatment of cystic fibrosis (CF) in patients aged 2 years and older who have at least one F508del mutation in the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) gene or a mutation in the CFTR gene that is responsive based on in vitro data.
If the patient’s genotype is unknown, an FDA-cleared CF mutation test should be used to confirm the presence of at least one F508del mutation or a mutation that is responsive based on in vitro data.
- Assessments of liver function tests (ALT, AST, and bilirubin) are recommended prior to initiating TRIKAFTA, every 3 months during the first year of treatment, and annually thereafter
- In the event of significant elevations in liver function tests, e.g. ALT or AST >5x the upper limit of normal (ULN) or ALT or AST >3x ULN with bilirubin >2x ULN, dosing should be interrupted and laboratory tests closely followed until the abnormalities resolve. Following the resolution of liver function test elevations, consider the benefits and risks of resuming treatment
- For patients with a history of hepatobiliary disease or liver function test elevations, more frequent monitoring should be considered
Hypersensitivity Reactions, Including Anaphylaxis
- Hypersensitivity reactions, including cases of angioedema and anaphylaxis, have been reported in the postmarketing setting. If signs or symptoms of serious hypersensitivity reactions develop during treatment, discontinue TRIKAFTA and institute appropriate therapy. Consider the benefits and risks for the individual patient to determine whether to resume treatment with TRIKAFTA
Concomitant Use With CYP3A Inducers
- Exposure to ivacaftor is significantly decreased and exposure to elexacaftor and tezacaftor are expected to decrease by the concomitant use of strong CYP3A inducers, which may reduce the therapeutic effectiveness of TRIKAFTA. Co‑administration with strong CYP3A inducers is not recommended
Concomitant Use With CYP3A Inhibitors
- Exposure to elexacaftor, tezacaftor, and ivacaftor are increased when co-administered with strong or moderate CYP3A inhibitors. The dose of TRIKAFTA should be reduced when used concomitantly with moderate or strong CYP3A inhibitors
Cataracts
- Cases of non-congenital lens opacities have been reported in pediatric patients treated with ivacaftor-containing regimens. Baseline and follow‑up ophthalmological examinations are recommended in pediatric patients initiating treatment with TRIKAFTA
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Serious Adverse Reactions
- Serious adverse reactions that occurred more frequently in patients treated with TRIKAFTA compared to placebo were rash (1% vs <1%) and influenza (1% vs 0)
Most Common Adverse Reactions
- The most common adverse reactions occurring in ≥5% of patients treated with TRIKAFTA (N=202) and higher than placebo (N=201) by ≥1% in the 24-week placebo-controlled, parallel-group Phase 3 trial (Trial 1) were headache, upper respiratory tract infection, abdominal pain, diarrhea, rash, alanine aminotransferase increased, nasal congestion, blood creatine phosphokinase increased, aspartate aminotransferase increased, rhinorrhea, rhinitis, influenza, sinusitis, and blood bilirubin increased
- The safety profile for the patients with CF receiving TRIKAFTA (N=55) enrolled in the 4-week, randomized, double-blind, active-controlled Phase 3 trial (Trial 2) was similar to that observed in Trial 1
- The safety profile in patients age 6 through 11 years from an open-label trial (Trial 3; N=66) was similar to that observed in Trial 1. The safety profile in patients age 2 through 5 years from an open-label trial (Trial 4; N=75) was similar to that observed in Trial 1
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pediatric Use
- The safety and effectiveness of TRIKAFTA in patients with CF younger than 2 years of age have not been established
Click here to access full Prescribing Information for TRIKAFTA.