DOSING INFORMATION
Recommended dosing for patients aged 2 to <6 years1
- Morning and evening doses should be taken approximately 12 hours apart
- Food or drink containing grapefruit should be avoided during treatment with TRIKAFTA
| Weight | ||
|---|---|---|
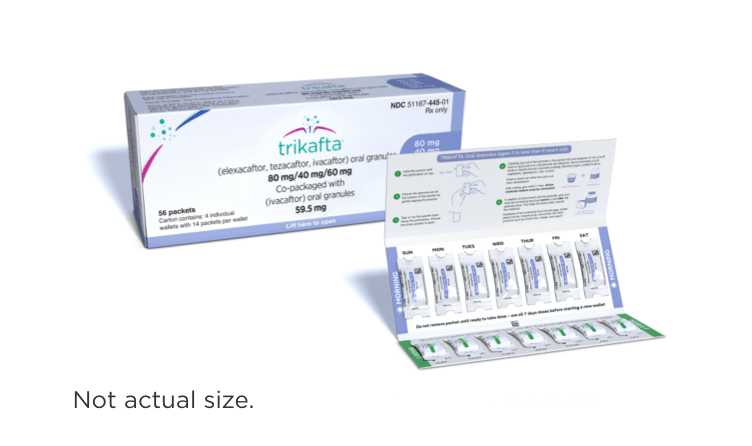
| <14 kg (<31 lb)1,2 | 1 white and blue packet of: elexacaftor 80 mg/ tezacaftor 40 mg/ ivacaftor 60 mg | 1 white and green packet of: ivacaftor 59.5 mg |
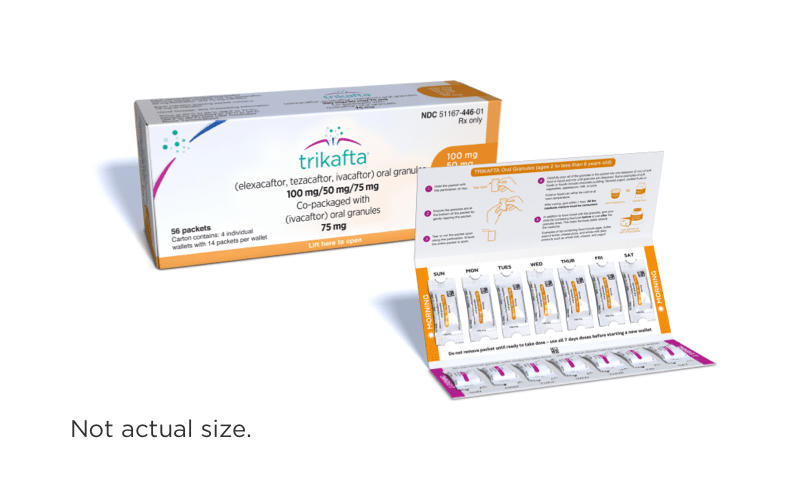
| ≥14 kg (≥31 lb)1,2 | 1 white and orange packet of: elexacaftor 100 mg/ tezacaftor 50 mg/ ivacaftor 75 mg | 1 white and pink packet of: ivacaftor 75 mg |
|
|
- Elexacaftor, tezacaftor, and ivacaftor oral granules are white to off-white, sweetened, unflavored granules approximately 2 mm in diameter
- Ivacaftor oral granules are white to off-white, sweetened, unflavored granules approximately 2 mm in diameter
ADMINISTRATION
How to administer oral granule doses of TRIKAFTA1
Preparation |
Examples of soft foods or liquids include:
Note: Use thickened food/purée in younger patients who are adjusting to solid foods. |
Administration |
|
Give fat-containing food |
Note: The list above includes only examples. Parents/caretakers can try other fat- containing foods that work best for the patient. Food or drink containing grapefruit should be avoided during treatment with TRIKAFTA. |
Preparation |
|---|
Examples of soft foods or liquids include:
Note: Use thickened food/purée in younger patients who are adjusting to solid foods. |
Administration |
|---|
|
Give fat-containing food |
|---|
Note: The list above includes only examples. Parents/caretakers can try other fat- containing foods that work best for the patient. Food or drink containing grapefruit should be avoided during treatment with TRIKAFTA. |
It is important for patients to consume the entire dose of granules within 1 hour after mixing
DOSING ADJUSTMENTS
Dose adjustments for hepatic impairment in patients aged 2 to <6 years1
| In patients with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class A) | NO DOSE ADJUSTMENT
|
| In patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class B) | TREATMENT IS NOT RECOMMENDED USE SHOULD ONLY BE CONSIDERED WHEN THERE IS A CLEAR MEDICAL NEED AND THE BENEFITS ARE EXPECTED TO OUTWEIGH THE RISKS If used, TRIKAFTA should be used with caution at a reduced dose, as follows:
Repeat above dosing schedule each week. The evening dose of the ivacaftor granules should not be taken.
|
| In patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C) | SHOULD NOT BE USED
|
| In patients with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class A) |
NO DOSE ADJUSTMENT
|
| In patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class B) |
TREATMENT IS NOT RECOMMENDED USE SHOULD ONLY BE CONSIDERED WHEN THERE IS A CLEAR MEDICAL NEED AND THE BENEFITS ARE EXPECTED TO OUTWEIGH THE RISKS If used, TRIKAFTA should be used with caution at a reduced dose, as follows:
Repeat above dosing schedule each week. The evening dose of the ivacaftor granules should not be taken.
|
| In patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C) |
SHOULD NOT BE USED
|
Dose adjustments for renal impairment in patients aged 2 to <6 years
- No dose adjustment is recommended in patients with mild (eGFR 60 to <90 mL/min/1.73 m2) or moderate (eGFR 30 to <60 mL/min/1.73 m2) renal impairment. TRIKAFTA has not been studied in patients with severe renal impairment or end-stage renal disease and should be used with caution in these patients1
Drug interaction profiles and related dosing considerations for patients aged 2 to <6 years
| Weight | Drug Interaction Profile | Dosing Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| <14 kg (<31 lb)1,2 | Strong CYP3A inducers including1: rifampin, rifabutin, phenobarbital, carbamazepine, phenytoin, St. John's wort (Hypericum perforatum) | CONCOMITANT USE NOT RECOMMENDED |
| Strong CYP3A inhibitors including1: ketoconazole, itraconazole, posaconazole, voriconazole, telithromycin, clarithromycin | IN THE MORNING (TWICE A WEEK)
NO PACKET IN THE EVENING | |
| Moderate CYP3A inhibitors including1: fluconazole, erythromycin | ALTERNATE GRANULES EVERY MORNING2
NO PACKET IN THE EVENING | |
| ≥14 kg (≥31 lb)1,2 | Strong CYP3A inducers including1: rifampin, rifabutin, phenobarbital, carbamazepine, phenytoin, St. John’s wort (Hypericum perforatum) | CONCOMITANT USE NOT RECOMMENDED |
| Strong CYP3A inhibitors including1: ketoconazole, itraconazole, posaconazole, voriconazole, telithromycin, clarithromycin | IN THE MORNING (TWICE A WEEK)
NO PACKET IN THE EVENING | |
| Moderate CYP3A inhibitors including1: fluconazole, erythromycin | ALTERNATE GRANULES EVERY MORNING2
NO PACKET IN THE EVENING |
| Weight |
|---|
| <14 kg (<31 lb)1,2 |
Drug Interaction Profile Strong CYP3A inducers including1: rifampin, rifabutin, phenobarbital, carbamazepine, phenytoin, St. John's wort (Hypericum perforatum) Dosing Considerations CONCOMITANT USE |
Drug Interaction Profile Strong CYP3A inhibitors including1: ketoconazole, itraconazole, posaconazole, voriconazole, telithromycin, clarithromycin Dosing Considerations IN THE MORNING (TWICE A WEEK)
NO PACKET IN THE EVENING |
Drug Interaction Profile Moderate CYP3A inhibitors including1: Dosing Considerations ALTERNATE GRANULES EVERY MORNING2
NO PACKET IN THE EVENING |
| Weight |
|---|
| ≥14 kg (≥31 lb)1,2 |
Drug Interaction Profile Strong CYP3A inducers including1: rifampin, rifabutin, phenobarbital, carbamazepine, phenytoin, St. John's wort (Hypericum perforatum) Dosing Considerations CONCOMITANT USE |
Drug Interaction Profile Strong CYP3A inhibitors including1: ketoconazole, itraconazole, posaconazole, voriconazole, telithromycin, clarithromycin Dosing Considerations IN THE MORNING (TWICE A WEEK)
NO PACKET IN THE EVENING |
Drug Interaction Profile Moderate CYP3A inhibitors including1: Dosing Considerations ALTERNATE GRANULES EVERY MORNING2
NO PACKET IN THE EVENING |
For more information about specific drug interactions and adjustment recommendations, see the Drug-Drug Interactions Tool.
MISSED DOSE
What to do if a dose is missed1
MISSED MORNING DOSE
- If ≤6 hours have passed, take as soon as possible and take evening dose as scheduled
- If >6 hours have passed, take the missed dose as soon as possible but do not take evening dose and continue as scheduled the following day
MISSED EVENING DOSE
- If ≤6 hours have passed, take as soon as possible and take next morning dose as scheduled
- If >6 hours have passed, do not take missed dose and take next morning dose as scheduled the following day
- If ≤6 hours have passed, take as soon as possible and take evening dose as scheduled
- If >6 hours have passed, take the missed dose as soon as possible but do not take evening dose and continue as scheduled the following day
- If ≤6 hours have passed, take as soon as possible and take next morning dose as scheduled
- If >6 hours have passed, do not take missed dose and take next morning dose as scheduled the following day
Morning and evening doses should not be taken at the same time
eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; lb, pounds.
aContinue dosing with 1 elexacaftor/tezacaftor/ivacaftor packet twice a week, approximately 3 to 4 days apart.1
bContinue dosing with 1 elexacaftor/tezacaftor/ivacaftor packet and 1 ivacaftor packet on alternate days.1
cContinue dosing with 2 elexacaftor/tezacaftor/ivacaftor tablets twice a week, approximately 3 to 4 days apart.1
dContinue dosing with 2 elexacaftor/tezacaftor/ivacaftor tablets and 1 ivacaftor tablet on alternate days.1
DOSING INFORMATION
Recommended dosing for patients aged 6 to <12 years1
- Morning and evening doses should be taken approximately 12 hours apart
- Food or drink containing grapefruit should be avoided during treatment with TRIKAFTA
| Weight | ||
|---|---|---|
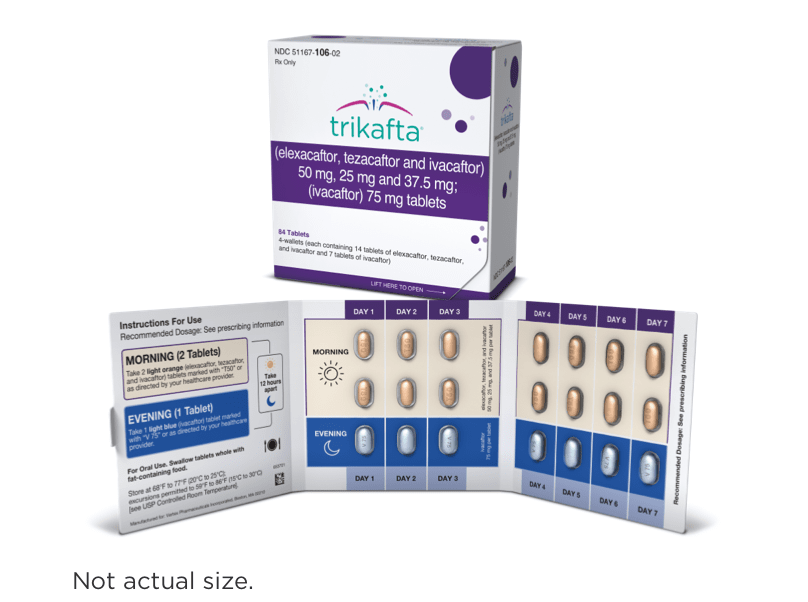
| <30 kg (<66 lb)1,2 | 2 light orange tablets of: elexacaftor 50 mg/ tezacaftor 25 mg/ ivacaftor 37.5 mg | 1 light blue tablet of: ivacaftor 75 mg |
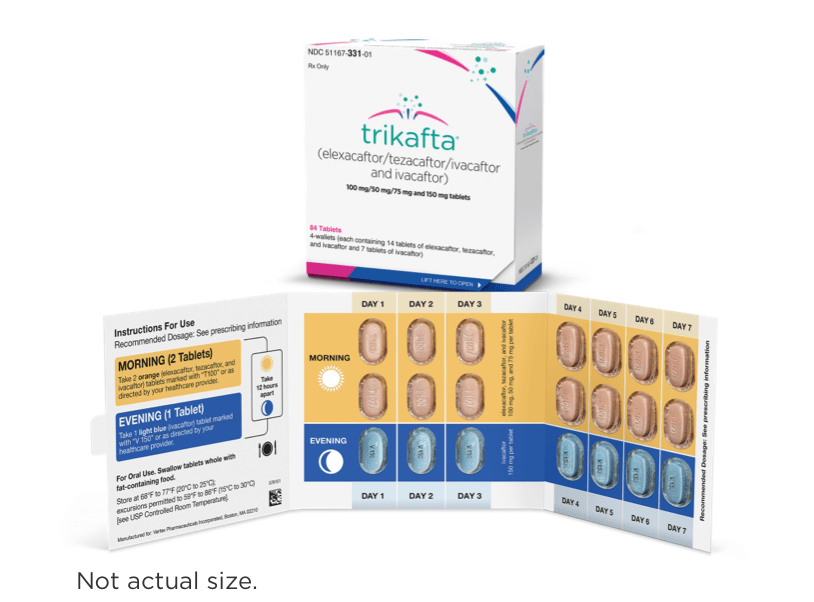
| ≥30 kg (≥66 lb)1,2 | 2 orange tablets of: elexacaftor 100 mg/ tezacaftor 50 mg/ ivacaftor 75 mg | 1 light blue tablet of: ivacaftor 150 mg |
|
|
- Elexacaftor 50 mg, tezacaftor 25 mg, and ivacaftor 37.5 mg tablets are light orange, capsule-shaped, and debossed with “T50” on one side and plain on the other
- Ivacaftor 75 mg tablets are light blue, film-coated, capsule-shaped, and printed with “V 75” in black ink on one side and plain on the other
- Elexacaftor 100 mg, tezacaftor 50 mg, and ivacaftor 75 mg tablets are orange, capsule-shaped, and debossed with “T100” on one side and plain on the other
- Ivacaftor 150 mg tablets are light blue, film-coated, capsule-shaped, and printed with “V 150” in black ink on one side and plain on the other
DOSING ADJUSTMENTS
Dose adjustments for hepatic impairment in patients aged 6 to <12 years1
| In patients with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class A) | NO DOSE ADJUSTMENT
|
| In patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class B) | TREATMENT IS NOT RECOMMENDED USE SHOULD ONLY BE CONSIDERED WHEN THERE IS A CLEAR MEDICAL NEED AND THE BENEFITS ARE EXPECTED TO OUTWEIGH THE RISKS If used, TRIKAFTA should be used with caution at a reduced dose, as follows:
Continue alternating Day 1 and Day 2 dosing thereafter No evening dose of ivacaftor should be taken
|
| In patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C) | SHOULD NOT BE USED
|
| In patients with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class A) |
NO DOSE ADJUSTMENT
|
| In patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class B) |
TREATMENT IS NOT RECOMMENDED USE SHOULD ONLY BE CONSIDERED WHEN THERE IS A CLEAR MEDICAL NEED AND THE BENEFITS ARE EXPECTED TO OUTWEIGH THE RISKS If used, TRIKAFTA should be used with caution at a reduced dose, as follows:
Continue alternating Day 1 and Day 2 dosing thereafter No evening dose of ivacaftor should be taken
|
| In patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C) |
SHOULD NOT BE USED
|
Dose adjustments for renal impairment in patients aged 6 to <12 years
- No dose adjustment is recommended in patients with mild (eGFR 60 to <90 mL/min/1.73 m2) or moderate (eGFR 30 to <60 mL/min/1.73 m2) renal impairment. TRIKAFTA has not been studied in patients with severe renal impairment or end-stage renal disease and should be used with caution in these patients1
Drug interaction profiles and related dosing considerations for patients aged 6 to <12 years
| Weight | Drug Interaction Profile | Dosing Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| <30 kg (<66 lb)1,2 | Strong CYP3A inducers including1: rifampin, rifabutin, phenobarbital, carbamazepine, phenytoin, St. John's wort (Hypericum perforatum) | CONCOMITANT USE NOT RECOMMENDED |
| Strong CYP3A inhibitors including1: ketoconazole, itraconazole, posaconazole, voriconazole, telithromycin, clarithromycin | IN THE MORNING (TWICE A WEEK)
NO TABLET IN THE EVENING | |
| Moderate CYP3A inhibitors including1: fluconazole, erythromycin | ALTERNATE TABLETS EVERY MORNING
NO TABLET IN THE EVENING | |
| ≥30 kg (≥66 lb)1,2 | Strong CYP3A inducers including1: rifampin, rifabutin, phenobarbital, carbamazepine, phenytoin, St. John’s wort (Hypericum perforatum) | CONCOMITANT USE NOT RECOMMENDED |
| Strong CYP3A inhibitors including1: ketoconazole, itraconazole, posaconazole, voriconazole, telithromycin, clarithromycin | IN THE MORNING (TWICE A WEEK)
NO TABLET IN THE EVENING | |
| Moderate CYP3A inhibitors including1: fluconazole, erythromycin | ALTERNATE TABLETS EVERY MORNING2
NO TABLET IN THE EVENING |
| Weight |
|---|
| <30 kg (<66 lb)1,2 |
Drug Interaction Profile Strong CYP3A inducers including1: rifampin, rifabutin, phenobarbital, carbamazepine, phenytoin, St. John's wort (Hypericum perforatum) Dosing Considerations CONCOMITANT USE |
Drug Interaction Profile Strong CYP3A inhibitors including1: ketoconazole, itraconazole, posaconazole, voriconazole, telithromycin, clarithromycin Dosing Considerations IN THE MORNING (TWICE A WEEK)
NO TABLET IN THE EVENING |
Drug Interaction Profile Moderate CYP3A inhibitors including1: Dosing Considerations ALTERNATE TABLETS EVERY MORNING
NO TABLET IN THE EVENING |
| Weight |
|---|
| ≥30 kg (≥66 lb)1,2 |
Drug Interaction Profile Strong CYP3A inducers including1: rifampin, rifabutin, phenobarbital, carbamazepine, phenytoin, St. John's wort (Hypericum perforatum) Dosing Considerations CONCOMITANT USE |
Drug Interaction Profile Strong CYP3A inhibitors including1: ketoconazole, itraconazole, posaconazole, voriconazole, telithromycin, clarithromycin Dosing Considerations IN THE MORNING (TWICE A WEEK)2
NO TABLET IN THE EVENING |
Drug Interaction Profile Moderate CYP3A inhibitors including1: Dosing Considerations ALTERNATE TABLETS EVERY MORNING2
NO TABLET IN THE EVENING |
For more information about specific drug interactions and adjustment recommendations, see the Drug-Drug Interactions Tool.
MISSED DOSE
What to do if a dose is missed1
MISSED MORNING DOSE
- If ≤6 hours have passed, take as soon as possible and take evening dose as scheduled
- If >6 hours have passed, take the missed dose as soon as possible but do not take evening dose and continue as scheduled the following day
MISSED EVENING DOSE
- If ≤6 hours have passed, take as soon as possible and take next morning dose as scheduled
- If >6 hours have passed, do not take missed dose and take next morning dose as scheduled the following day
- If ≤6 hours have passed, take as soon as possible and take evening dose as scheduled
- If >6 hours have passed, take the missed dose as soon as possible but do not take evening dose and continue as scheduled the following day
- If ≤6 hours have passed, take as soon as possible and take next morning dose as scheduled
- If >6 hours have passed, do not take missed dose and take next morning dose as scheduled the following day
Morning and evening doses should not be taken at the same time
eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; lb, pounds.
aContinue dosing with 1 elexacaftor/tezacaftor/ivacaftor packet twice a week, approximately 3 to 4 days apart.1
bContinue dosing with 1 elexacaftor/tezacaftor/ivacaftor packet and 1 ivacaftor packet on alternate days.1
cContinue dosing with 2 elexacaftor/tezacaftor/ivacaftor tablets twice a week, approximately 3 to 4 days apart.1
dContinue dosing with 2 elexacaftor/tezacaftor/ivacaftor tablets and 1 ivacaftor tablet on alternate days.1
12 Years and Older
DOSING INFORMATION
Recommended dosing for patients aged 12 years and older1
- Morning and evening doses should be taken approximately 12 hours apart
- Food or drink containing grapefruit should be avoided during treatment with TRIKAFTA
For patients aged 12 years and older1
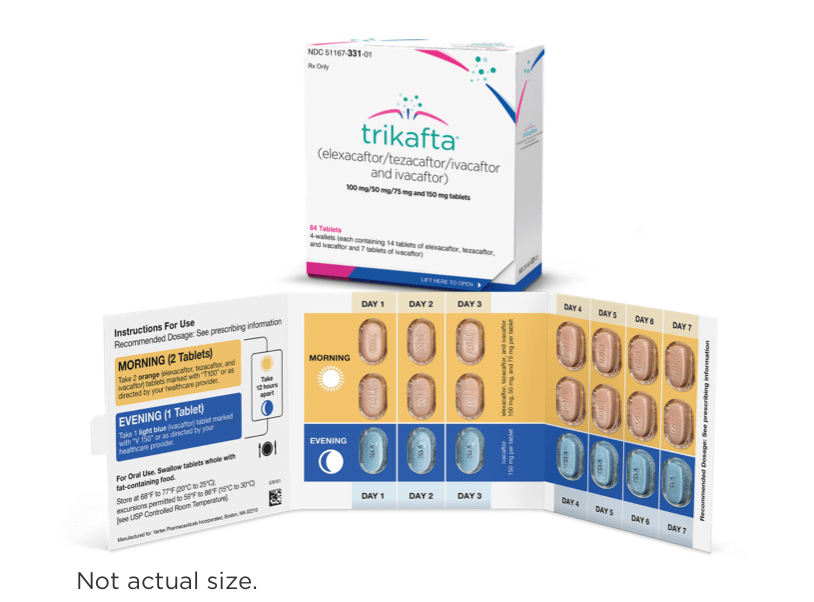
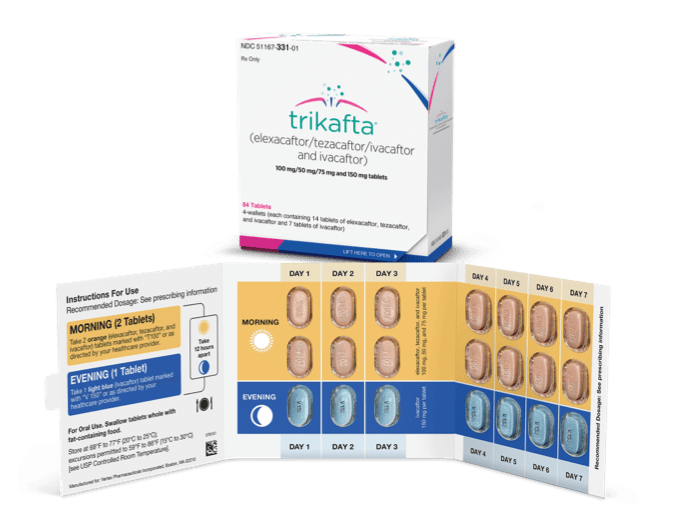
| 2 orange tablets of: elexacaftor 100 mg/ tezacaftor 50 mg/ ivacaftor 75 mg | 1 light blue tablet of: ivacaftor 150 mg |
|
- Elexacaftor, tezacaftor, and ivacaftor tablets are orange, capsule-shaped, and debossed with “T100” on one side and plain on the other
- Ivacaftor tablets are light blue, film-coated, capsule-shaped, and printed with “V 150” in black ink on one side and plain on the other
DOSING ADJUSTMENTS
Dose adjustments for hepatic impairment in patients aged 12 years and older1
| In patients with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class A) | NO DOSE ADJUSTMENT
|
| In patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class B) | TREATMENT IS NOT RECOMMENDED USE SHOULD ONLY BE CONSIDERED WHEN THERE IS A CLEAR MEDICAL NEED AND THE BENEFITS ARE EXPECTED TO OUTWEIGH THE RISKS If used, TRIKAFTA should be used with caution at a reduced dose, as follows:
Continue alternating Day 1 and Day 2 dosing thereafter No evening dose of ivacaftor should be taken
|
| In patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C) | SHOULD NOT BE USED
|
| In patients with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class A) |
NO DOSE ADJUSTMENT
|
| In patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class B) |
TREATMENT IS NOT RECOMMENDED USE SHOULD ONLY BE CONSIDERED WHEN THERE IS A CLEAR MEDICAL NEED AND THE BENEFITS ARE EXPECTED TO OUTWEIGH THE RISKS If used, TRIKAFTA should be used with caution at a reduced dose, as follows:
Continue alternating Day 1 and Day 2 dosing thereafter No evening dose of ivacaftor should be taken
|
| In patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C) |
SHOULD NOT BE USED
|
Dose adjustments for renal impairment in patients aged 12 years and older
- No dose adjustment is recommended in patients with mild (eGFR 60 to <90 mL/min/1.73 m2) or moderate (eGFR 30 to <60 mL/min/1.73 m2) renal impairment. TRIKAFTA has not been studied in patients with severe renal impairment or end-stage renal disease and should be used with caution in these patients1
Drug interaction profiles and related dosing considerations for patients aged 12 years and older
| Drug Interaction Profile | Dosing Considerations |
|---|---|
| Strong CYP3A inducers including1: rifampin, rifabutin, phenobarbital, carbamazepine, phenytoin, St. John's wort (Hypericum perforatum) | CONCOMITANT USE |
| Strong CYP3A inhibitors including1: ketoconazole, itraconazole, posaconazole, voriconazole, telithromycin, clarithromycin | IN THE MORNING (TWICE A WEEK)
NO TABLET IN THE EVENING |
| Moderate CYP3A inhibitors including1: fluconazole, erythromycin | ALTERNATE TABLETS EVERY MORNING
NO TABLET IN THE EVENING |
Drug Interaction Profile Strong CYP3A inducers including1: rifampin, rifabutin, phenobarbital, carbamazepine, phenytoin, St. John's wort (Hypericum perforatum) Dosing Considerations CONCOMITANT USE |
Drug Interaction Profile Strong CYP3A inhibitors including1: ketoconazole, itraconazole, posaconazole, voriconazole, telithromycin, clarithromycin Dosing Considerations IN THE MORNING (TWICE A WEEK)
NO TABLET IN THE EVENING |
Drug Interaction Profile Moderate CYP3A inhibitors including1: Dosing Considerations ALTERNATE TABLETS EVERY MORNING
NO TABLET IN THE EVENING |
For more information about specific drug interactions and adjustment recommendations, see the Drug-Drug Interactions Tool.
MISSED DOSE
What to do if a dose is missed1
MISSED MORNING DOSE
- If ≤6 hours have passed, take as soon as possible and take evening dose as scheduled
- If >6 hours have passed, take the missed dose as soon as possible but do not take evening dose and continue as scheduled the following day
MISSED EVENING DOSE
- If ≤6 hours have passed, take as soon as possible and take next morning dose as scheduled
- If >6 hours have passed, do not take missed dose and take next morning dose as scheduled the following day
- If ≤6 hours have passed, take as soon as possible and take evening dose as scheduled
- If >6 hours have passed, take the missed dose as soon as possible but do not take evening dose and continue as scheduled the following day
- If ≤6 hours have passed, take as soon as possible and take next morning dose as scheduled
- If >6 hours have passed, do not take missed dose and take next morning dose as scheduled the following day
Morning and evening doses should not be taken at the same time
eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; lb, pounds.
aContinue dosing with 1 elexacaftor/tezacaftor/ivacaftor packet twice a week, approximately 3 to 4 days apart.1
bContinue dosing with 1 elexacaftor/tezacaftor/ivacaftor packet and 1 ivacaftor packet on alternate days.1
cContinue dosing with 2 elexacaftor/tezacaftor/ivacaftor tablets twice a week, approximately 3 to 4 days apart.1
dContinue dosing with 2 elexacaftor/tezacaftor/ivacaftor tablets and 1 ivacaftor tablet on alternate days.1
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Elevated Transaminases and Hepatic Injury
- Liver failure leading to transplantation has been reported in a patient with cirrhosis and portal hypertension while receiving TRIKAFTA. Avoid use of TRIKAFTA in patients with pre-existing advanced liver disease (e.g., as evidenced by cirrhosis, portal hypertension, ascites, hepatic encephalopathy) unless the benefits are expected to outweigh the risks. If used in these patients, they should be closely monitored after the initiation of treatment
- Isolated elevations of transaminases or bilirubin have been observed in patients with CF treated with TRIKAFTA. In some instances, transaminase elevations have been associated with concomitant elevations in total bilirubin and/or international normalized ratio (INR) and have resulted in patients being hospitalized for intervention, including in patients without a history of pre-existing liver disease
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
TRIKAFTA is indicated for the treatment of cystic fibrosis (CF) in patients aged 2 years and older who have at least one F508del mutation in the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) gene or a mutation in the CFTR gene that is responsive based on in vitro data.
If the patient’s genotype is unknown, an FDA-cleared CF mutation test should be used to confirm the presence of at least one F508del mutation or a mutation that is responsive based on in vitro data.
- Assessments of liver function tests (ALT, AST, and bilirubin) are recommended prior to initiating TRIKAFTA, every 3 months during the first year of treatment, and annually thereafter
- In the event of significant elevations in liver function tests, e.g. ALT or AST >5x the upper limit of normal (ULN) or ALT or AST >3x ULN with bilirubin >2x ULN, dosing should be interrupted and laboratory tests closely followed until the abnormalities resolve. Following the resolution of liver function test elevations, consider the benefits and risks of resuming treatment
- For patients with a history of hepatobiliary disease or liver function test elevations, more frequent monitoring should be considered
Hypersensitivity Reactions, Including Anaphylaxis
- Hypersensitivity reactions, including cases of angioedema and anaphylaxis, have been reported in the postmarketing setting. If signs or symptoms of serious hypersensitivity reactions develop during treatment, discontinue TRIKAFTA and institute appropriate therapy. Consider the benefits and risks for the individual patient to determine whether to resume treatment with TRIKAFTA
Concomitant Use With CYP3A Inducers
- Exposure to ivacaftor is significantly decreased and exposure to elexacaftor and tezacaftor are expected to decrease by the concomitant use of strong CYP3A inducers, which may reduce the therapeutic effectiveness of TRIKAFTA. Co‑administration with strong CYP3A inducers is not recommended
Concomitant Use With CYP3A Inhibitors
- Exposure to elexacaftor, tezacaftor, and ivacaftor are increased when co-administered with strong or moderate CYP3A inhibitors. The dose of TRIKAFTA should be reduced when used concomitantly with moderate or strong CYP3A inhibitors
Cataracts
- Cases of non-congenital lens opacities have been reported in pediatric patients treated with ivacaftor-containing regimens. Baseline and follow‑up ophthalmological examinations are recommended in pediatric patients initiating treatment with TRIKAFTA
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Serious Adverse Reactions
- Serious adverse reactions that occurred more frequently in patients treated with TRIKAFTA compared to placebo were rash (1% vs <1%) and influenza (1% vs 0)
Most Common Adverse Reactions
- The most common adverse reactions occurring in ≥5% of patients treated with TRIKAFTA (N=202) and higher than placebo (N=201) by ≥1% in the 24-week placebo-controlled, parallel-group Phase 3 trial (Trial 1) were headache, upper respiratory tract infection, abdominal pain, diarrhea, rash, alanine aminotransferase increased, nasal congestion, blood creatine phosphokinase increased, aspartate aminotransferase increased, rhinorrhea, rhinitis, influenza, sinusitis, and blood bilirubin increased
- The safety profile for the patients with CF receiving TRIKAFTA (N=55) enrolled in the 4-week, randomized, double-blind, active-controlled Phase 3 trial (Trial 2) was similar to that observed in Trial 1
- The safety profile in patients age 6 through 11 years from an open-label trial (Trial 3; N=66) was similar to that observed in Trial 1. The safety profile in patients age 2 through 5 years from an open-label trial (Trial 4; N=75) was similar to that observed in Trial 1
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pediatric Use
- The safety and effectiveness of TRIKAFTA in patients with CF younger than 2 years of age have not been established
Click here to access full Prescribing Information for TRIKAFTA.
References:
1. TRIKAFTA [prescribing information]. Boston, MA: Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated; August 2023. 2. Data on file. Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated. Boston, MA. REF-6607 (v2.0); 2021.